How to get rid of moisture and mushroom from home?
When can the mushroom appear at home?
The correct, "healthy" humidity in the rooms is 30-65%, at 20-22 ° C.When it is higher - it exceeds 80% and persists for several days - conditions arise to conducive to the development of mold and other mushrooms.These grow best at 20-30 ° C, but they are not bothering at home.They have low nutritional requirements and high adaptation skills - they are able to develop on almost every ground: wood, fabrics, plasters ...
We will notice them when green, brown or black eruptions appear on the walls, and in the apartment we will sense an unpleasant, musty smell that cannot be ventilated.Their spores floating in the air cause serious respiratory diseases, allergies, muscle and joint pain, fatigue, nose -lived, breathing problems and many other ailments, up to stomach, esophagus or blood.In this context, it is clearly visible how important for the health of the household it is to prevent moisture of the building.
Where does moisture come from at home?
W wyniku kapilarnego podciągania woda sięga do 1,5 m, lecz może i cztery razy więcej!Zawilgocenie konstrukcji budynku może być efektem przecieków - to pierwszy i najbardziej oczywisty trop. Przeciekać może nieszczelny dach, bo np. stare pokrycie z blachy przerdzewiało albo pseudofachowcy ułożyli nowe niezgodnie ze sztuką. Woda może przenikać także przez taras nad pomieszczeniem - w naszych warunkach klimatycznych, większość hydroizolacji wytrzyma tam bez napraw kilka, góra kilkanaście lat.Sometimes rainwater floods the walls - because the gutters cannot keep up with it or just clogged.The area around the chimneys, due to leaky flashings, are a typical place of leaks.In each of these cases, wet spots, stains, then mold will appear on the ceiling or walls.
Water also rubs from below.In old buildings, there is often a lack of horizontal moisture insulation of foundations and floors on the ground, which allows capillary pulling of moisture from the ground (this is the ability of materials to transport water upwards).Even if the foundations are insulated with moisture, water can break down at the place of damage/discontinuity of insulation.It is even more difficult to properly insulate basements.In this case, insulation must be adapted to the type of ground and groundwater level - their design should take into account the conditions on a specific plot.
When the water penetrates from the ground, it may not be easy to find a point where it gets into the building.Water is guided where it encounters the slightest resistance - the place where it reveals can be a few meters away from the source.The transport of moisture in the walls as a result of its capillary pull -up usually reaches up to 1.5 m, but it can even be - depending on the type of soil, groundwater level, material from which the wall was built, its thicknesses - and four times more!Its symptoms are not only moist spots inside the building, but also salt efflorescence on the facade.
Tu woda dostaje się do budynku od dołu - izolacja przeciwilgociowa jest uszkodzona albo w ogóle jej nie ma. (fot. Archiwum BD)Wet stains on the wall will appear as a result of damage to the water, sewage or heating installation - e.g. after accidental drilling of the pipe during renovation or when hanging images.Alternatively after unsealing the old or carelessly made installation.On the other hand, such a stain is not always the effect of leaks or leaks.Water is also introduced to the interior of its inhabitants.A family of 4 - breathing, cooking, pending - produces it within a day from 10 to 15 liters.
If the interiors are underheated, the walls are not insulated, and the ventilation does not work, water vapor from the air drizzled on the coldest fragments of partitions - walls, ceilings.This is where the stains will be created, which incorrectly takes the result of some leaks.
Understanding this phenomenon facilitates the concept of relative humidity, which - by simplifying the matter - describes how much water vapor is in the air.The maximum amount of steam in the air at a certain temperature is 100%, the higher the temperature, the more steam it can absorb.After exceeding 100%, the pair begins to condense.
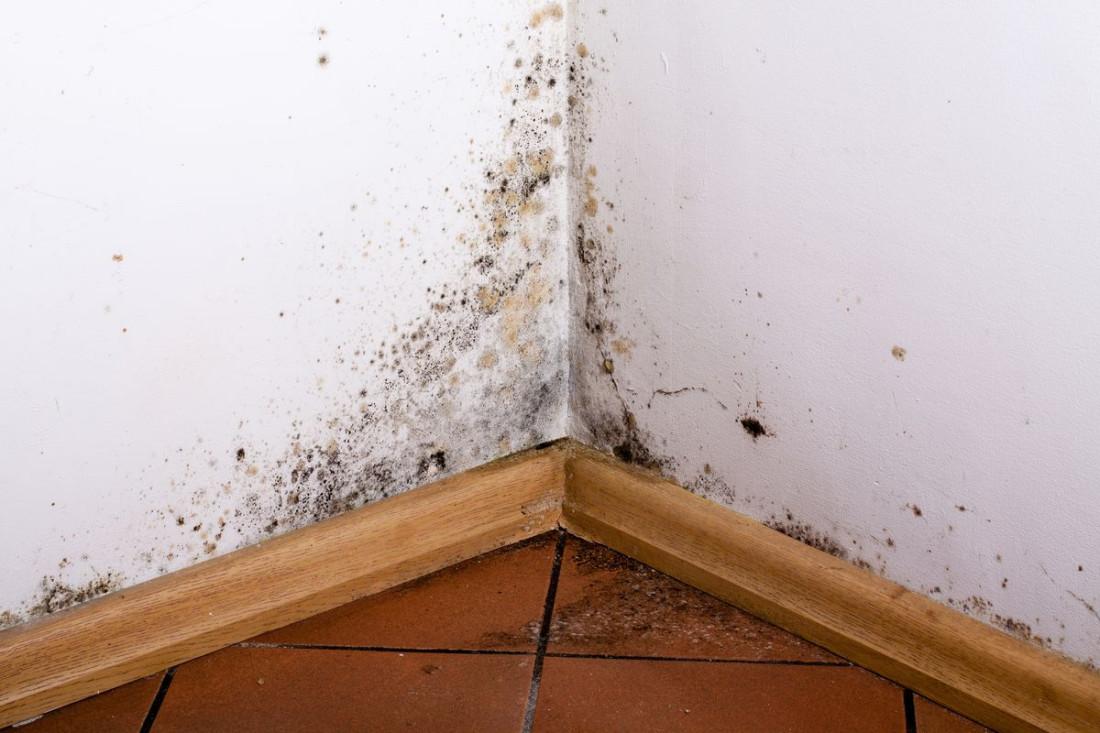

In a well -functioning house, moist air is constantly escaping efficient ventilation.If it is blocked (e.g. by clogging boxes), the amount of moisture in the air will grow, because people produce it constantly.Therefore, it will inevitably exceed 100%, and then sprinkle in the coldest places, usually where thermal bridges occur.Which means that the lack of efficient ventilation condemns the building to moisture.Which, in turn, leads to the appearance of mushrooms that threaten the health of people staying in it.A bright signal of too high humidity are long -lasting stem mirrors or sleepless towels in the bathroom.
Importantly, water vapor can be condensed not only on the surface of the partitions, but also inside them.A lot of attention should be paid to insulation of roof slopes on a utility attic.Mineral wool is usually used here as thermal insulation.It should be separated from the room by a vapor -tight foil, which prevents the steam prevents insulation.If "professionals" have forgotten about its arrangement or did it carelessly, sooner or later we will have a problem.In this part of the house you can make more mistakes, which after a few years result in moisture of roof insulation and even its structure.One of them may be the lack of ventilation gaps.
If a high vapor permeability foil is laid on the roof, one gap is enough - between the foil and covering.When the foil has a low vapor permeability or instead of it was given to the roofing roofing (or full formwork covered with foil), two gaps are needed - one between insulation and foil, the other between the foil and covering.The gaps must be expensive all over their height from the inlet in the eaves to the outlet in the ridge.
In places where dormers, chimneys and roof windows interrupt them, you need to use additional tiles or ventilation fireplaces.If the roof ventilation is defective, water vapor will sprinkle from the inside of the foil or formwork.
The couple also penetrates the walls.You need to know that the diffusion resistance (i.e. the ability of the material to stop it) of individual layers of the wall (load -bearing layer, insulation, plaster) should decrease towards the outside.Then the couple simply penetrate the wall.Otherwise, it will propose in its cross -section at the interface of layers.If such moisture is not enough, it will evaporate in the summer season.If there is more of it - there will be a permanent moisture of the wall.
Moisture in the building
Depending on when it goes to the building, moisture is divided into 3 types:
How to fight the moisture of the walls?
Efficient ventilation is key to restore and maintain proper humidity in the interior.We discussed this issue in more detail in the previous text.If the source of the moisture of the building and the appearance of mold are leaks or executive errors, you need to start with their removal.The fight against mushrooms without eliminating the cause of their invasion will only give short -term results.
First, we repair leaky roofing, clean or replace the gutters, repair leaky water or sewage system.A difficult operation is to restore/perform horizontal moisture insulation between the foundation and walls.In houses without basements, their contact is cut, then polyethylene plates, sheet metal, foil or roofing felt are inserted into the gap.This is a complicated and expensive job, you should hire specialists.It carries the risk of violating the building structure, and the problem is also bypassing the installation in the walls.
Capillary water pull -ups are also prevented by realizing the alternative method - injection.This involves injecting chemicals into the wall that form an insulating layer.Unfortunately - especially in the case of thick and heterogeneous walls - it is difficult to get tight insulation in this way.
Żeby odtworzyć poziomą izolację przeciwilgociową podcina się ściany nośne nad fundamentamiThese methods cut off moisture pulling, but do not dry the walls.Here again efficient ventilation and heating are needed, or the use of dehumidifiers.Such high -performance devices are definitely more effective than the weathering itself.They are also quite expensive, but they can be rented.
It is also necessary to ensure that it is the renovation that does not contribute to the moisture of the house.If new, brick partitions or concrete screed are made in the building, a significant amount of water goes inside.It is then necessary to clearly increase the weathering intensity combined with stronger heating.Many investors are warming with foamed polystyrene.This is material with high diffusion resistance - if we cover it with wet walls, moisture will be stopped in the building.Therefore, it would be good to dry the walls first.
When insulating the walls with mineral wool, pay attention to the type of plaster - wool is vapor permeable, so external plaster should also have a low diffusion resistance coefficient so that moisture does not stay in the thermal insulation layer.For this reason, the popular acrylic plaster is not arranged on it.
Lack or improper thermal insulation is of great importance with the aforementioned condensation of water vapor on the coldest fragments of partitions.This phenomenon occurs in places of thermal bridges, i.e. where the heat from the room escapes particularly intensively.The cause of their formation is usually design or executive errors.If the reason for moisture is the careless arrangement of insulation - the insulation must be cut and rewritten.A single -layer wall can simply be warmed (which will make it double -layer).
PoradnikCenisz nasze porady? Możesz otrzymywać najnowsze w każdy czwartek!How to remove mushrooms from home?
If mold fungi appeared only on the surface of the wall, it must be cleaned with water, scrubbing with a brush with stiff bristles and after drying apply the fungicide.When the mushroom attacked deeper, the plaster is scraped or caught.
The wall cleans and disinfects (e.g. with water with a preparation with chlorine), drought, and later protects with fungicides, which should deeply penetrate into the ground.They should be used in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions, observing the safety rules.If we want to apply smooth or paint on the fucked up wall - choose those with fungicidal ingredients.
Wykwity pleśni szoruje się szczotką ze sztywnym włosiem. Po wysuszeniu na ścianę nakłada się środek grzybobójczy. (fot. Fotolia)In more complex cases, it is better to entrust the fight against mushrooms to professionals.They will be able to identify the species that attacked the house and choose the most effective fungicide.
Wooden surfaces attacked by mold are also cleaned with a brush, and after drying it is covered with a fungicidal preparation.If the fungus reaches deeper, the wood should be sharpened.After drying and solid impregnation, they can be painted with paint, stain or varnish.Flagized elements should also be intensively heated (after cleaning) with an electric heater or a sunflower.Heating with a temperature of up to 60-70 ° C kills mushrooms and drying the ground.
Janusz Wernerfot.Opening: Fotolia