Soot fire in the chimney - proceedings - Strazacki.pl portal about the fire brigade
As every year, during the heating season, firefighters have their hands full during events related to soot fires in chimney ducts. Building fires and carbon monoxide poisoning, commonly known as carbon monoxide, often occur through a faulty chimney duct. How to prevent and deal with a soot fire? You will learn about it in the material below.
Often, soot fires are caused by the negligence of chimney users. The basic and most important mistake is not cleaning the chimney flues from solid fuel stoves. However, that's not all. Burning garbage, plastic, wet wood in the stove also leads to the deposition of soot particles. Soot can settle over the entire height of the chimney or only a certain part, thus reducing the clearance of the chimney. In extreme cases, soot deposits can completely block the flue.
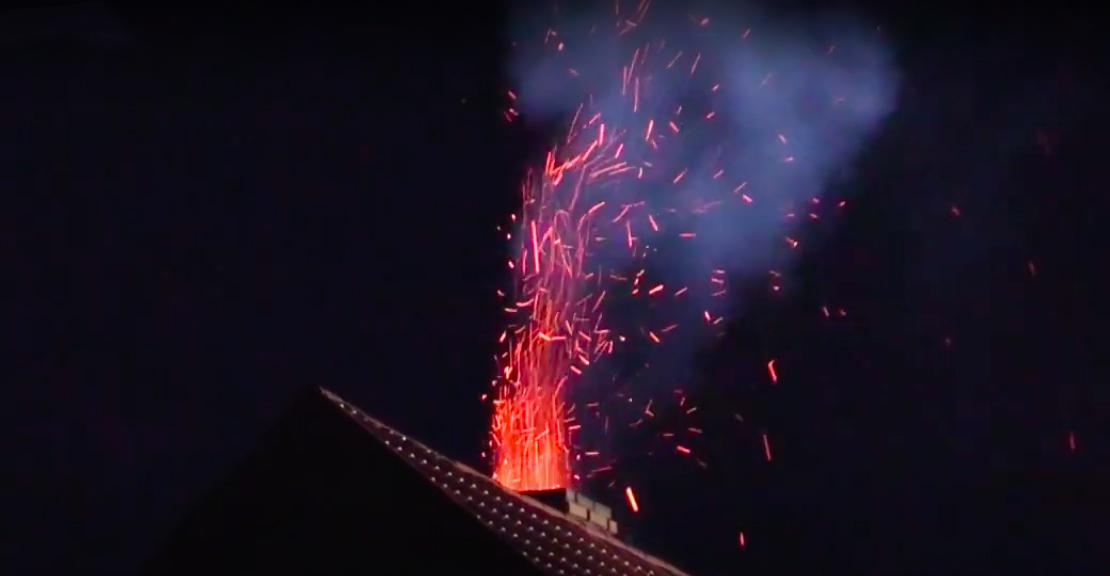
photo: example of a soot fire in a chimney. < /td> |
Before the heating season as well as during it, the owner or manager of the building should thoroughly inspect the technical condition of the chimney duct. The patency and tightness of the chimney should be checked. Accumulated soot should be removed immediately, and if cracks are found in the pipe, they should be repaired. The best way to check the chimney and clean it is to order it to a professional, i.e. a chimney sweep.
Soot burning at high temperatures can cause cracks and leaks in the chimney duct. Flying fires visible at the mouth of the chimney or a flame that looks a bit like a burner flame are also visible. High temperature or flames coming from the chimney crevices can ignite the materials surrounding the flue. Smoke or carbon monoxide can also enter living quarters through cracks.
| photo: Soot particles that settle on the surface of the flue. |
Proceedings of the user, owner or manager of the buildingWhen soot ignites in the chimney duct, we should evacuate the building and inform the fire brigade about this event. If possible, close the air supply to the stove both from the bottom and from the top. It is important not to pour water into a burning chimney. One liter of H2O produces as much as 1700 liters of steam, which unfortunately can lead to cracking of the hose and even its tearing. After the fire brigade has completed the activities, follow the instructions received from the Head of the Rescue Operation ("action commander"). The most common written recommendation will be not to use the stove and flue until it has been cleaned and inspected by a chimney sweep. Failure to comply with these recommendations, re-lighting the fire in the stove and possible further threat to other users may result in penal consequences specified in the Penal Code in Article 160 § 1. (Whoever exposes a person to a direct danger of loss of life or serious health, shall be subject to the penalty of deprivation of liberty for up to 3 years)
Fire brigade conduct! IMPORTANT ! The described techniques of action are not a procedure and steps of direct action. The head of the rescue operation determines the priorities of actions in accordance with the situation at the scene of the incident. It is also recommended to undergo stationary training in order to comprehensively assimilate the topic.
1) Extinguishing the furnaceThis is an important element of the activities of the fire protection unit. Extinguishing the furnace consists in removing all combustible material from the furnace hearth. We remove the material from the hearth with a metal furnace shovel into a metal bucket. Then we take the burning or glowing material outside the object. When taking out this material, let's pay attention to whether we cause smoke in the rooms through which we leave. To minimize the risk of smoke in the rooms, we can use a fire blanket, which we put on a metal bucket. Extinguishing the furnace by a group of firefighters should be done with the use of breathing apparatus or filter masks.
2) Extinguishing sootSoot can be extinguished from the side of the chimney duct outlet located on the roof of the building or from the cleaning hole located at the lowest point of the chimney (usually the basement). To reach the chimney outlet, we can use a technical hatch located on the roof of the building, portable ladders, mechanical ladders or lifts. In a situation where there is or may be ice on the pitched roof, soot extinguishing activities should be carried out from the basket of a mechanical ladder or lift. The technique of extinguishing soot from the outlet side may consist in installing a chimney sieve, throwing dry sand or extinguishing powder (in the form of so-called bombs) into the chimney extinguishing powder - extinguishing powder in the amount of about 0.5 kg in a plastic bag) or mechanical precipitation of soot with the use of a chimney sweeper. Extinguishing soot from the cleanout side consists in feeding a stream of powder from a powder extinguisher up the chimney or giving a highly dispersed stream of water using special dedicated chimney lances for this purpose.
3) Removal of soot from the cleanout This is generally a procedure carried out after or simultaneously with the removal of soot from the chimney duct. As in the case of removing combustible material from the hearth, soot from the cleaning pit should be removed with a metal shovel into a metal bucket. Apply a fire blanket over the soot bucket if necessary.

4) Using a thermal imaging cameraWith a thermal imaging camera, we check the walls in places where the chimney duct runs in order to check whether there is probably still soot in the chimney and to determine the effectiveness of our actions (you should compare the heat signature visible on the camera's display every several minutes; the decreasing and fading heat signature testifies to the effectiveness of actions). The camera can also be used to check the chimney from the outlet side. It is not recommended to use pyrometers to check walls in case of soot fires in chimneys.
photo: Thermal image with visible heat signature of the flue. Also visible is the place where the remaining soot is probably burning (yellow color).
|
photo: Thermal image of the inside of the chimney after the soot is extinguished. No soot burning heat signature. |
5) Monitoring the atmosphere in the building Due to the possibility of carbon monoxide being present in the building, penetrating through possible cracks in the chimney, it is necessary to systematically monitor the atmosphere using meters single or multi-gas with a carbon monoxide detector. If carbon monoxide is detected, KDR should consider evacuating residents. Ventilate the building by opening all windows and doors. At the very end of the activities, the atmosphere should be checked again for the possibility of carbon monoxide with measuring devices. The final check of the atmosphere should be done with the windows and doors closed. All observed values and their absence at the end of the activities should be included in the report prepared by the State Fire Service after returning to the base. For people with symptoms indicating possible carbon monoxide poisoning, appropriate PSP procedures should be implemented.
6) Checking the ceilingsFire brigade activities should also consist of physical and thermal camera inspection of the building's ceilings at the point where the chimney passes. This is very important for wooden or combustible ceilings. Possible cracks in the chimney may lead to fire of the wooden ceiling structure or combustible filling. If, for example, a thermal imaging camera detects a heat signature that may indicate a fire hazard, part of the ceiling should be dismantled to reveal the possible fire hazard. The decision on demolition is made only by the Head of the Rescue Operation.
Legal acts regulating matters related to chimney ducts:
I. Act of July 7, 1994 Construction Law. Maintenance of buildings: Art. 61. The owner or manager of the building is obliged to maintain and use the building in accordance with the rules referred to in Art. 5 sec. 2.Art. 62. 1. Objects should be subjected during their use by the owner or administrator: 1) periodic inspection, at least once a year, consisting in checking the technical condition of: factors occurring during the use of the facility, b) installations and devices for environmental protection, c) gas installations and chimney ducts (smoke, combustion and ventilation); 2) periodic inspections, at least once every 5 years, consisting in checking the technical condition and suitability for use the use of the building, the aesthetics of the building and its surroundings; this inspection should also cover the examination of the electrical and lightning protection installation in terms of the efficiency of connections, accessories, protection and means of protection against electric shock, insulation resistance of wires and earthing of installations and devices.
II. Regulation of the Minister of the Interior and Administration of 07 June 2010 on fire protection of buildings, other construction facilities and areas § 34. 1. In facilities or parts thereof, where the combustion of solid, liquid or gaseous fuel takes place, contamination from smoke and flue gas ducts during their periods of use: 1) from furnaces of collective catering establishments and catering services - at least once a month, unless local regulations provide otherwise; 2) from furnaces fired with solid fuel not listed in point 1 - at least once for 3 months;3) from furnaces fired with liquid and gaseous fuel not listed in point 1 - at least once every 6 months.2. In the facilities or their parts referred to in par. 1, dirt is removed from the ventilation ducts at least once a year, if the higher frequency does not result from the operating conditions.3. The activities referred to in par. 1 and 2 are carried out by people with chimney sweep qualifications.4. The provision of sec. 3 does not apply to the removal of pollutants from the smoke, exhaust and ventilation ducts of single-family residential buildings and buildings of homestead and holiday homes. (IN ALL, IT IS RECOMMENDED TO CLEAN THE CABLES ONCE EVERY 6 MONTHS)
Strazacki.pl